User feedback is at the core of usability testing and product design. So, defining the types of user feedback is essential. Understanding how users interact with a product and gathering their insights can lead to valuable improvements in user experience (UX).
Whether you’re refining a website, mobile app, or physical product, collecting and analyzing feedback ensures that your product meets user needs and preferences.
In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of user feedback for usability testing, how to collect it effectively, and how to choose the right feedback method for your business.
What is User Feedback?
User feedback refers to the information and insights gathered from users regarding their experiences with a product, service, or system. In the context of usability testing, it plays a crucial role in understanding how users interact with a design, what challenges they face, and how they perceive the overall experience.
Effective user feedback can guide improvements, enhance user satisfaction, and ultimately lead to a more successful product.
User feedback can take various forms, including verbal comments, written responses, metrics from user interactions, and emotional reactions observed during testing. By collecting and analyzing this feedback, designers, and developers can make informed decisions that align the product with user needs.
How to Collect User Feedback the Right Way?
Collecting user feedback the right way requires thoughtful planning and execution. Here are key steps to ensure you collect valuable customer feedback:
1. Define Your Objectives
Before collecting feedback, it’s essential to define the specific objectives. Are you testing a new feature, checking for usability issues, or measuring overall user satisfaction? Clear objectives will help you focus on gathering the right type of feedback.
2. Choose the Right Testing Methods
There are several ways to collect feedback during usability testing, including:
- In-person tests: Observe users while they interact with your product.
- Remote tests: Collecting feedback from users testing your product in their environment.
- Moderated or unmoderated sessions: Moderated sessions involve guiding the user through tasks, while unmoderated sessions let users interact freely.
- Automated tools: Analytics, heat maps, and other tools are used to gather data automatically.
3. Select a Diverse User Group
Gathering feedback from a representative sample of your target audience is important. A diverse group can help you uncover a wider range of usability issues, ensuring the product is user-friendly for different users.
4. Prepare a Set of Relevant Tasks
Users should perform tasks that align with their objectives to gather meaningful feedback. Well-designed tasks should simulate real-world usage scenarios, helping you observe how users navigate and interact with the product.
5. Gather and Analyze Feedback
Collect user feedback through direct observation, surveys, interviews, or analytics. Then, analyze the data to identify common patterns, usability issues, and areas for improvement. Focus on quantitative data (metrics, task success rates) and qualitative data (comments, suggestions).
Why Use Different User Feedback Types?
Utilizing various types of user feedback is essential for a well-rounded understanding of user experiences. Each feedback type offers unique insights and serves different purposes. Here’s why diversity in feedback types matters:
- Exclusive Insights: Different feedback methods capture different dimensions of user experience. While surveys may provide numerical data on user satisfaction, interviews can reveal the emotions and motivations behind those numbers. A combination of both gives a fuller picture.
- Identifying Trends and Issues: Relying solely on one type of feedback may result in blind spots. For example, analytics tools may indicate a drop in user engagement, but interviews may uncover the underlying reasons. Combining feedback types can help identify trends and pinpoint issues more effectively.
- Enhancing Engagement: Users may prefer different modes of providing feedback. Offering multiple feedback options ensures you engage a broader range of users, increasing the likelihood of capturing valuable insights.
- Validating Findings: Various feedback methods allow for cross-validation of findings. For instance, if survey results indicate high satisfaction but usability testing reveals significant issues, further investigation is warranted.
6 Types of User Feedback
Understanding the various types of user feedback is vital for effective usability testing. Here are some common types:
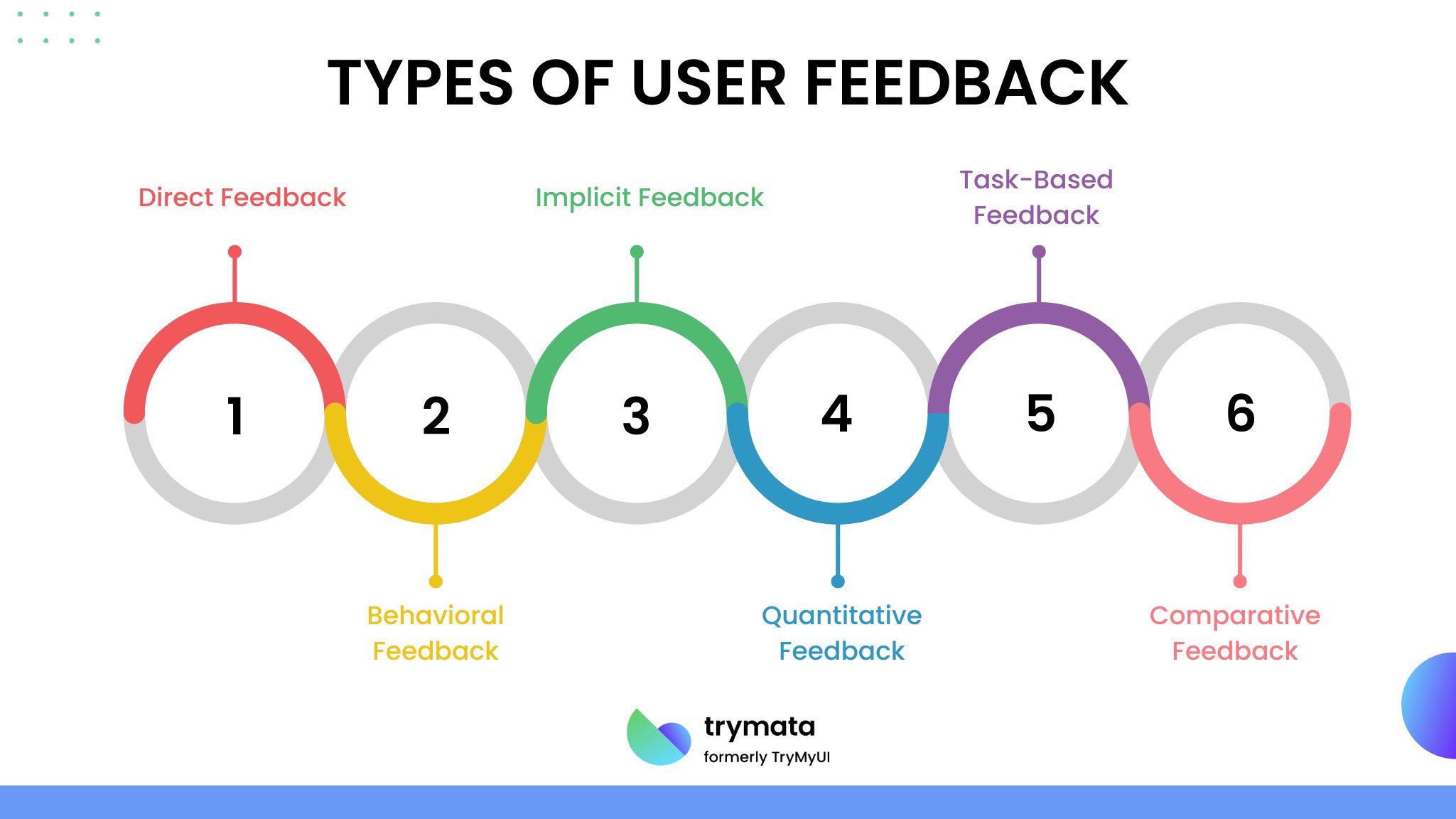
1. Direct Feedback
Direct feedback involves users sharing their thoughts and opinions explicitly. It can include:
- Think-Aloud Protocols: Users verbalize their thoughts as they interact with the product, providing insights into their decision-making processes.
- Post-Test Interviews: Users can reflect on their experiences after usability tests, allowing for deeper insights into their interactions.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Structured surveys can quantify user satisfaction and gather specific insights.
2. Behavioral Feedback
Behavioral feedback focuses on user actions and interactions. Key methods include:
- Observational Feedback: Observing users as they interact with a product reveals how they navigate and where they encounter difficulties.
- Task Success and Failure Rates: Tracking the completion rates of tasks helps identify usability issues.
- Time on Task: Measuring how long it takes users to complete tasks can highlight areas of confusion.
3. Implicit Feedback
Implicit feedback captures users’ emotional reactions and non-verbal cues. This can include:
- Emotional Reactions: Noting body language and facial expressions during interactions can provide context to user satisfaction or frustration.
- Eye Tracking: Analyzing where users focus their attention can reveal which design elements capture interest or cause confusion.
4. Quantitative Feedback
Quantitative feedback involves measurable data that can be analyzed statistically. Key aspects include:
- Metrics and Analytics: Analyzing error rates and user flows helps quantify usability issues.
- System Usability Scale (SUS): A standardized tool to measure usability that provides a score based on user responses.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using analytics to inform design choices based on user behavior.
5. Task-Based Feedback
Task-based feedback focuses on specific user tasks and their experiences. This includes:
- Critical Incident Reporting: Users report significant issues they encountered during tasks, helping identify major usability problems.
- Satisfaction Ratings: Users rate their satisfaction after completing specific tasks, providing insight into their experiences.
6. Comparative Feedback
Comparative feedback involves comparing different versions of a product or design elements. This can include:
- A/B Testing: Comparing two product versions to determine which performs better based on user interactions.
- Preference Testing: Asking users to compare features or designs to understand user preferences.
Choose the Best User Feedback for Your Business
To determine the best user feedback type for your business, consider the following factors:
- Business Goals: Are you looking to improve a customer satisfaction score, enhance product features, or increase user retention? Align your feedback type with your specific business objectives.
- Resources Available: Some feedback methods, like interviews and focus groups, require more time and resources than simpler methods like NPS surveys. Ensure your chosen feedback type is manageable within your team’s capacity.
- Target Audience: Consider your users’ demographics and communication preferences. Younger audiences respond more to social media feedback, while enterprise clients prefer in-depth interviews.
- Scalability: Certain feedback methods are more scalable than others. If you need insights from a large user base, consider surveys or NPS scores, which are easier to distribute and analyze at scale.
- Type of Feedback Needed: Tools like NPS, behavioral analytics, and surveys are ideal for quantitative insights. If you need deeper qualitative data, consider focus groups or user interviews.
Conclusion
User feedback is a critical component of usability testing. It provides valuable insights that drive product improvements and enhance user experience. By understanding the various types of user feedback and employing the right collection methods, businesses can make informed decisions that lead to more effective products.
Whether through direct feedback, behavioral observations, implicit reactions, quantitative metrics, task-based evaluations, or comparative assessments, each type of feedback contributes to a fuller understanding of user needs.
By strategically choosing the best feedback methods for your business, you can ensure that your product meets and exceeds user expectations, ultimately leading to greater satisfaction and loyalty.