Delivering a seamless user experience is essential for the success of any product or service. Usability evaluation is a cornerstone in understanding and improving how real users interact with your product.
By observing users perform specific tasks, gathering feedback, and analyzing usability metrics, teams can identify usability problems and refine their designs. This blog explores the importance of usability evaluation, its methods, and how it differs from usability testing.
You’ll also discover actionable insights into recruiting participants, overcoming challenges, and leveraging user research to enhance user satisfaction and drive better product development outcomes.
What is Usability Evaluation?
Usability testing is a systematic process for determining how target users can use a product, system, or service to achieve their goals. We observe real users performing tasks, collect data on their performance, and identify usability issues.
This process is key to a good user experience (UX) and ensuring the design meets user needs. Unlike usability testing, which is often task—and scenario-based, usability evaluation involves a broader set of techniques, including heuristics and inspection.
When to Use Usability Evaluation?
Usability evaluation can be conducted at various stages of the design process to ensure a user-friendly interface. It is particularly useful:
- During the Initial Design Phase: Identify potential usability issues early and align the design with user needs.
- Before Launch: To ensure the product meets user expectations and usability metrics.
- Post-Launch: To gather feedback from existing users and address any usability issues in real-world usage.
- Continuous Improvement: To refine the design system based on user feedback and web analytics.
Incorporating usability evaluation methods throughout the product development process ensures a seamless user experience and minimizes usability problems.
Importance of Usability Evaluation in User Experience (UX) Design
Usability evaluation is critical in UX design by providing actionable user behavior and preferences insights. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: Evaluating usability helps ensure users feel comfortable and confident using the product.
- Improved User Performance: Usability evaluation focuses on enabling users to complete tasks efficiently, reducing frustration.
- Increased Retention: Businesses can maintain existing users and attract new ones by addressing usability issues.
- Cost-Effective Development: Identifying and resolving usability problems early in the design process saves resources in the long run.
- Valuable Insights: The process helps teams understand user needs and preferences, driving better design decisions.
Difference Between Usability Testing vs Usability Evaluation
While usability testing and usability evaluation are closely related, they differ in scope and application:
| Aspect | Usability Testing | Usability Evaluation |
| Definition | Focuses on observing users perform tasks. | Encompasses a broader range of assessment methods. |
| Methods | Includes usability testing qualitative and quantitative usability testing. | Involves heuristic evaluation, usability inspection, and usability inquiry. |
| Scope | Centered on specific tasks and scenarios. | Includes both testing and broader design considerations. |
| Data Collection | Collects quantitative data and qualitative data. | Incorporates user feedback, usability metrics, and web analytics. |
Both usability testing and evaluation provide valuable insights that inform the design process and improve the user interface.
Types of Usability Evaluation
Usability evaluation is critical for ensuring that a product or system meets user needs effectively and efficiently. It involves various methods to assess how users interact with a product, identify pain points, and enhance user satisfaction. Here are the main types:
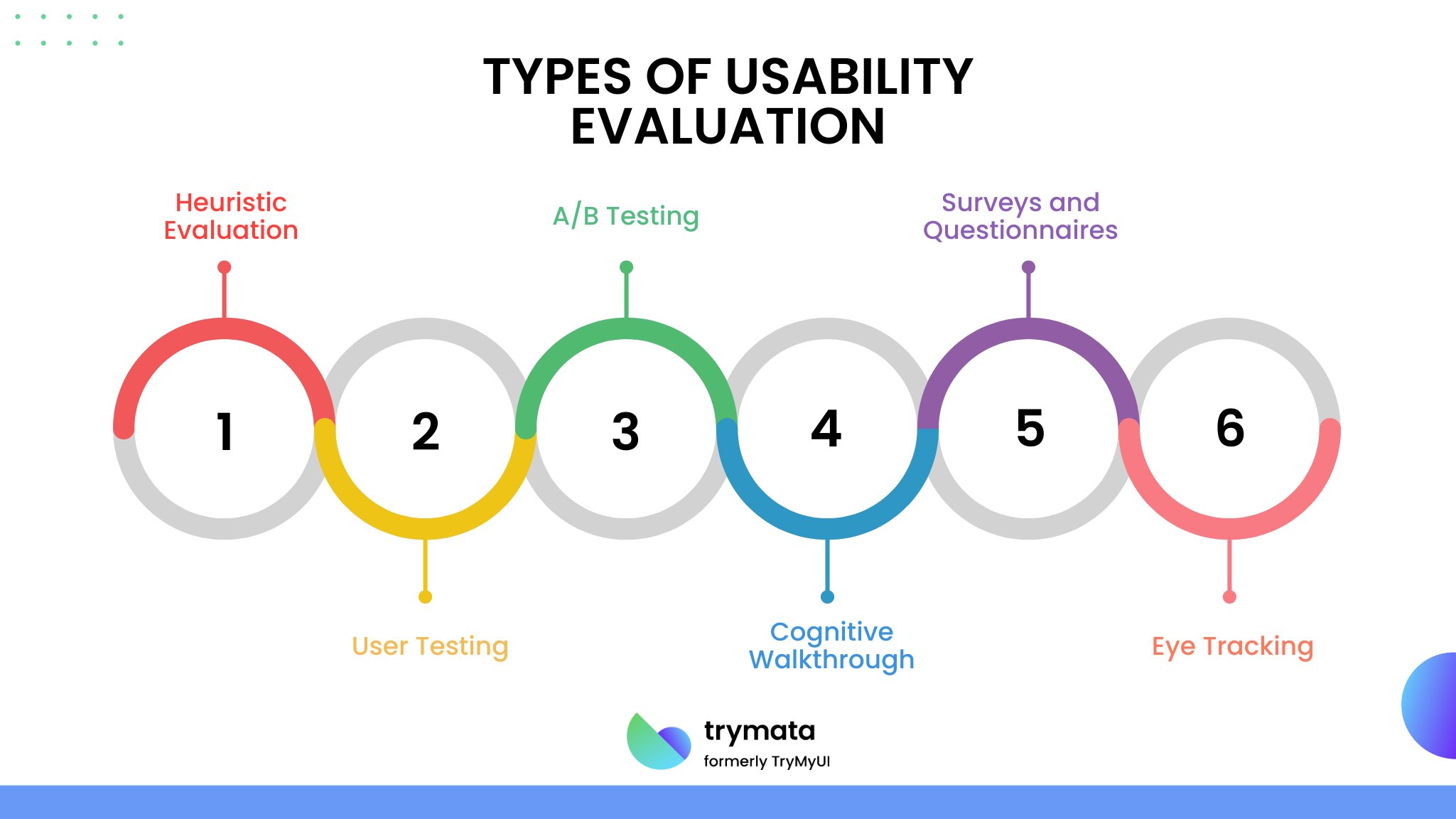
1. Heuristic Evaluation
In this method, usability experts evaluate a product against established usability principles, known as heuristics. Based on their expertise, they identify issues, focusing on consistency, feedback, and user control. This is a cost-effective way to uncover problems early in the design process.
2. User Testing
Real users interact with the product while performing specific tasks, as observed by researchers. This helps identify usability challenges and gather direct feedback. User testing can be done in remotely controlled environments or in the user’s natural context.
3. A/B Testing
This involves comparing two versions of a product or feature to determine which performs better. Users are split into groups, each using a different version, and their behavior is analyzed to make data-informed design decisions.
4. Cognitive Walkthrough
This method involves stepping through a product’s tasks as if the evaluator were the user, focusing on ease of learning. It’s particularly effective for first-time user experiences.
5. Surveys and Questionnaires
Collecting feedback through structured questions helps understand user satisfaction and gather insights on usability issues from a broader audience.
6. Eye Tracking
By monitoring where users focus their attention, eye-tracking provides valuable insights into how users visually navigate a product, revealing design areas that might need improvement.
Choosing the right method depends on your goals, timeline, and resources. Combining methods often yields the most comprehensive results, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
Usability Evaluation Methods
Usability evaluation methods are diverse, catering to different research objectives and target user groups.
- Qualitative Usability Testing: Focuses on subjective feedback through interviews and focus groups. It helps uncover users’ preferences, emotions, and challenges, offering rich, detailed insights.
- Quantitative Usability Testing: Collects measurable data like task success rates, time on task, and error counts. This method identifies patterns and benchmarks user performance.
- Heuristic Evaluation: Involves experts assessing the interface against usability guidelines to detect issues early without user involvement.
- Remote Usability Testing: Observes users in their natural environments using online tools, allowing for diverse and authentic feedback.
- Usability Inspection: Experts examine the product for potential usability problems, relying on professional judgment rather than user feedback.
- Usability Inquiry: Directly engages users by asking about their experiences, expectations, and suggestions. This method emphasizes user-centered insights.
By integrating these methods, teams can gather qualitative and quantitative data, comprehensively understanding usability challenges and driving user-centered design improvements.
How to Recruit Users for Usability Evaluation
Recruiting the right users is essential for an effective usability evaluation. It ensures the feedback gathered accurately represents the target audience’s needs, preferences, and pain points. Here are steps to recruit users effectively:
1. Define Your Target Audience
Clearly identify the user personas that reflect your product’s primary audience. Consider demographics, experience levels, and specific characteristics, such as industry or job roles, to ensure participants align with real-world users.
2. Choose Recruitment Methods
Utilize a mix of approaches to find participants. Common methods include:
- User Panels: Engage existing customers or users familiar with your product.
- Social Media and Forums: Post opportunities in relevant communities or professional groups.
- Recruitment Agencies: Use specialized agencies to find qualified participants quickly.
- Incentivized Surveys: Use short surveys to filter and attract potential participants.
3. Screen Participants
Implement a screening process to ensure candidates match your target criteria. Use screening questionnaires to gauge their familiarity with similar products or tasks, avoiding outliers who may not provide relevant insights.
4. Offer Incentives
Encourage participation by providing appropriate incentives, such as gift cards, discounts, or monetary rewards. Be clear about the commitment required and the benefits participants will receive.
5. Communicate Clearly
Provide participants with clear instructions, timelines, and expectations. Ensure they understand the usability evaluation’s purpose and their role in the process.
6. Build a Diverse Pool
Aim for diversity in demographics and experience levels to uncover a broad range of usability issues. This is especially important for products with a wide target audience.
By recruiting the right users, you can obtain valuable insights that lead to meaningful improvements and a more user-friendly product.
Benefits of Usability Evaluation
Usability evaluation offers several benefits for UX design and the product development process:
- Enhanced Design Process: Identifying usability problems early allows for iterative improvements.
- Informed Decision-Making: Quantitative research and qualitative research provide a balanced understanding of user needs.
- Improved User Satisfaction: Addressing usability issues ensures users feel more engaged and satisfied.
- Cost Savings: Resolving problems during the design process reduces the need for costly post-launch fixes.
- Actionable Insights: Usability evaluation methods yield insights that drive better product development.
- Competitive Advantage: A user-friendly product can differentiate your brand in a crowded market.
How to Deal with Common Usability Evaluation Challenges
Conducting usability evaluations can present challenges, but these can be addressed effectively:
- Limited Resources: Use remote usability testing and online tools to conduct evaluations cost-effectively.
- Recruiting Participants: Leverage social media and focus groups to find suitable participants.
- Subjective Feedback: Combine qualitative data with quantitative data to ensure balanced insights.
- Diverse User Needs: Involve diverse participants to identify patterns and cater to varied preferences.
- Interpreting Results: Use usability testing scripts and predefined metrics to ensure consistency.
- Technical Constraints: Choose testing tools compatible with your design system and product requirements.
Conclusion
Usability evaluation is an indispensable part of the product development process. By employing a mix of qualitative usability testing and quantitative usability testing, teams can gather valuable insights to enhance user experience. Incorporating remote testing, heuristic evaluation, and usability inquiry ensures a comprehensive evaluation process.
Ultimately, usability evaluation helps identify usability issues, improve user satisfaction, and create a product that meets user needs. Conducting usability testing with real users and observing their behavior provides actionable insights critical for a successful design process.
User Testing Script: Definition, Importance, Benefit & Template




