User-Centered Design (UCD) is a game-changing approach to creating products that genuinely resonate with users. By placing users’ needs, preferences, and challenges at the heart of the design process.
UCD ensures solutions that are not only functional but also intuitive and engaging. From usability testing to user feedback, every step prioritizes the real-world experiences of the intended audience.
This blog explores the key principles, benefits, and practical steps of User Centered Design, offering insights into how businesses can create products that delight users while achieving their goals.
What is User Centered Design?
User centered design (UCD) is an exceptional approach that puts users’ needs, preferences, and limitations at the forefront of the design and development process. It’s not just about aesthetics or functionality; it’s about creating meaningful and intuitive experiences involving users throughout every process stage.
The core idea of UCD is to prioritize the
- People who will use the product,
- Ensuring their goals,
- Tasks and challenges drive the design decisions.
This human-centered approach focuses on deeply understanding users through user research, usability testing, and iterative design.
By doing so, designers can create solutions that are not only effective but also enjoyable to use. UCD leads to designs that resonate with users because they address real problems and align with user expectations, ultimately fostering trust and satisfaction.
Importance of User-Centered Design
A user-centered approach benefits both businesses and their intended users. It bridges the gap between user and business goals by creating highly usable design solutions. Users interact with a product that aligns with their expectations and effectively solves their problems, reducing frustration and fostering loyalty.
Key benefits of UCD include:
- Enhanced usability for products designed with UCD makes them easier to use and understand.
- Reduced development costs for Identifying user problems early saves time and resources.
- Improved user satisfaction to meet user needs leads to better overall experiences.
- Increased accessibility to consider diverse user segments ensures inclusivity.
Principles of User Centered Design
To design products that truly meet user needs, it is essential to follow certain guiding principles. In this section, we outline the foundational principles of UCD and explain how they ensure a design process that prioritizes users at every step.
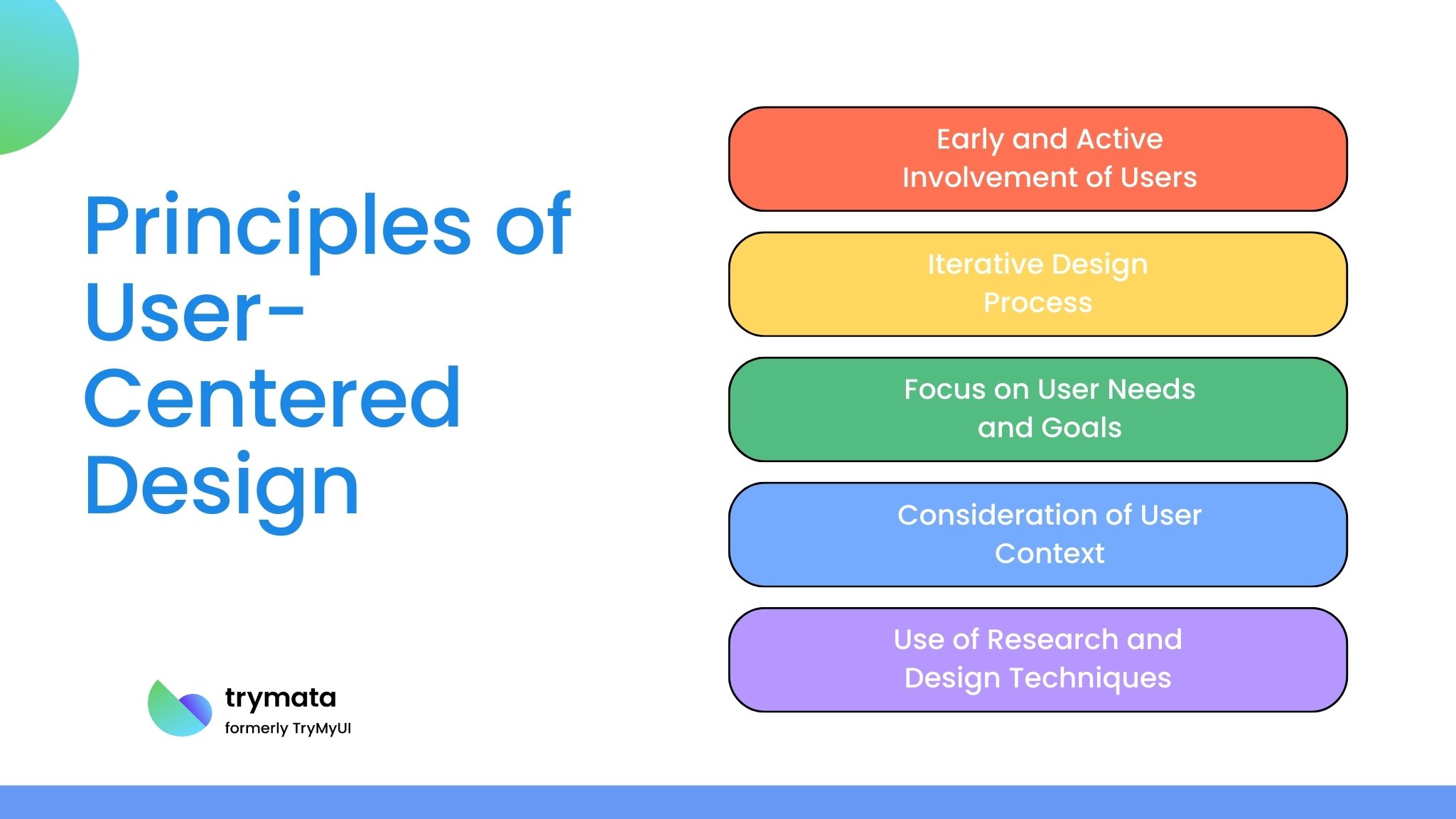
- Early and Active Involvement of Users: Involving users early in the design process helps identify user problems and ensure that design solutions align with user and task requirements.
- Iterative Design Process: Prototyping and user testing allow for refining designs based on real user interactions and feedback.
- Focus on User Needs and Goals: Understanding user behaviors, goals, and scenarios ensure the design meets intended users’ expectations.
- Consideration of User Context: Observing users and considering their environments leads to more practical and accessible solutions.
- Use of Research and Design Techniques: Employing user journey maps, personas, and both qualitative and quantitative data helps design solutions tailored to different user segments.
How to Create a User Centered Design Process
Developing a user-centered design process involves strategic steps to ensure that user needs are integrated at every stage. This section provides a step-by-step guide for teams to create products prioritizing usability and user satisfaction.
Step 1: Conduct User Research
This helps understand users’ needs, behaviors, and frustrations deeply. Remote usability testing can also provide insights into how users interact with your product. Begin by gathering user research data using methods such as
- Surveys,
- Interviews, and
- Focus groups.
Step 2: Define User Personas and Scenarios
The research data will be used to create user personas and scenarios. These tools represent user segments and help the design team understand the target audience’s needs and preferences.
Step 3: Map User Journeys
Develop user journey maps to visualize how users interact with the product. This step highlights pain points and areas for improvement.
Step 4: Ideate and Prototype
Generate design solutions through brainstorming and prototyping. Low-fidelity prototypes can quickly test ideas and gather feedback without significant investment.
Step 5: Usability Testing
Involve users in usability testing to evaluate how well the design aligns with user requirements. This iterative process identifies issues early and informs necessary adjustments.
Step 6: Iterate and Refine
Apply the iterative process to refine the design. By obtaining feedback from multiple rounds of user testing, the design evolves to meet user needs better.
Step 7: Implement and Monitor
Integrate the design into the product development process. After launch, continue to observe users and collect feedback to ensure continuous improvement.
How to Measure the Outcome of User Centered Design
How do you measure the success of a user centric design? Here are the methods and metrics:
1. Collect and Analyse User Feedback
Surveys, interviews, and focus groups were used to see how users perceived the product. Direct feedback gives you insight into user satisfaction and areas to improve.
2. Measure Usability Metrics
Task completion rates, time on task, error rates, and user satisfaction scores. These numbers give you an idea of how easy and efficient the design is.
3. Behavioural Data Analysis
Use analytics tools to see how users interact with the product. Track click-through rates, session duration, and navigation patterns to see user behavior and friction points.
4. Prototype Testing Comparisons
Test multiple prototypes to see usability improvements. Comparing test results from different stages of the iterative process shows progress and what remains to be solved.
5. Business Impact
Measure how well the design meets business goals, such as increased conversion rates, customer retention, and reduced support requests. Good UCD usually leads to better business performance.
6. Remote Usability Testing
Conduct remote testing sessions to see users in their environment. This will uncover real-world usability issues that may not appear in controlled testing.
7. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis
Combine metrics with user stories to get a complete picture of the design’s success. Quantitative data shows trends and outcomes, and qualitative data gives context and depth.
8. Continuous Improvement
After launch, track the product over time. Collect user feedback and revisit usability metrics regularly so the design can evolve with user needs.
So use these methods to know your user-centric design works for both users and the business. Measuring regularly creates a culture of continuous improvement and user-driven innovation.
User-Centered Design Example
Real-world examples can provide valuable insights into how UCD works in practice. This section walks you through a scenario where UCD principles transform a frustrating user experience into a seamless, intuitive process.
Imagine redesigning an e-commerce site with a search function that often frustrates users. A user-centered design strategy might involve:
- Conducting user research methods to identify user expectations and problems.
- Creating user personas to represent different user segments.
- Mapping user flows to understand how users search and browse.
- Prototyping and testing various search function designs.
- Observing users completing tasks to identify friction points.
- Iterating on the design to create a highly usable user interface.
Benefits of Implementing User Centered Design Principles
Adopting a user-centered approach comes with numerous advantages that directly impact both user experience and business outcomes:
- Positive User Experience: Products that prioritize users’ needs are intuitive and enjoyable and deliver seamless interactions, leaving a lasting impression on users.
- Reduced User Frustration: Identifying and addressing pain points early in the process ensures smoother interactions, reducing the likelihood of users abandoning the product.
- Increased User Loyalty: When users feel their needs are met, they’re more likely to engage repeatedly, fostering a loyal customer base and enhancing retention rates.
- Cost-Effective Design: Resolving usability issues during the early stages of the design and development process minimizes the need for costly redesigns or updates later, saving both time and resources.
- Accessible Solutions: Designing with diverse user segments in mind ensures inclusivity, expanding the product’s reach and accommodating the needs of all intended users.
By implementing these principles, businesses enhance usability and strengthen their competitive edge in the market.
Challenges in Implementing User centered design (UCD)
Despite its benefits, adopting a UCD process comes with challenges:
- Time and Resource Constraints: Conducting user research and testing requires significant investment.
- Balancing Priorities: Aligning user needs with business requirements can be complex.
- Stakeholder Buy-In: Convincing stakeholders of the value of a user-centered approach may require evidence.
- Iterative Nature: Continuous improvement demands ongoing commitment and resources.
Conclusion
User centered design is a game changer for creating user-friendly, impactful products. By putting users at the heart of the design process, UCD bridges the gap between user needs and business goals, resulting in solutions that increase satisfaction, usability, and accessibility. This leads to products that delight users and build loyalty and trust.
It’s not without its challenges that balancing priorities and getting stakeholder buy-in is hard, but the benefits far outweigh the effort. Early issue detection, cost-effective development, and stronger customer relationships are just a few of the outcomes that prove it.
Measurable success through usability metrics, feedback analysis, and behavioral data means continuous improvement and innovation. UCD means better user experiences and gives you a competitive advantage. When users feel heard and valued, they become loyal.